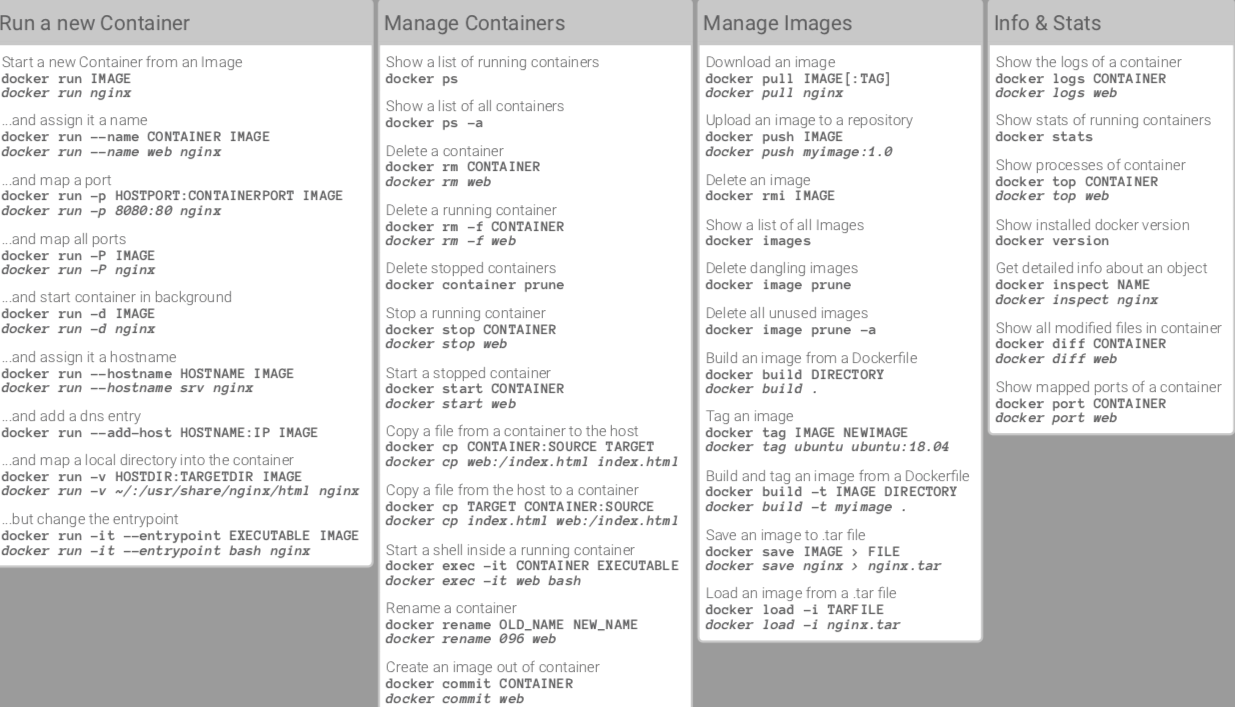
Docker Cheat Sheet This is Docker Cheat Sheet made for all developers. Docker is a set of the platform as a service product that uses OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Docker is an open-source platform that can be used to build, ship, and run applications by packaging software in containers. Docker has a lot of commands and options, and it is very difficult to remember every command. This article provides a cheat sheet of the most commonly used Docker commands. $ docker images REPOSITORY TAG ID ubuntu 12.10 b750fe78269d me/myapp latest 7b2431a8d968 $ docker images -a # also show intermediate Manages images. Docker rmi docker rmi b750fe78269d Deletes images. Clean up Clean all docker system prune Cleans up dangling images, containers, volumes, and networks (ie, not associated with a container). Docker container ls docker image ls docker ps docker ps -a docker run -it -p 8080:80 ubuntu:latest -name ubuntu-machine /bin/bash docker exec -it ubuntu-machine /bin/bash This is a probably the complete set of commands, that we use on daily basis.
- Cheat Sheet Dockers
- Docker Command Line Cheat Sheet
- Cheat Sheet Docker Compose
- Docker Build Cheat Sheet
- Owasp Cheat Sheet Docker
docker daemon
Enable buildkit
Add to /etc/docker/daemon.json:
docker-compose
Devices
Labels
External Network
Dockerfile
Docker Stop Signal
imagemagick
vim
path update
download & extract tar.gz
gpg dirmgr explained
purge
list what exposed ports do
cassandra
gosu
debian
copy with proper permissions
su-exec
setgid
npm
gosu
Cheat Sheet Dockers

tini
node
redis
docker
google cloud sdk
kubectl
pip
locale
tomcat
https://github.com/Unidata/tomcat-docker/blob/master/Dockerfile
gosu tomcat
Secure repository setup
create application folder structure
Download and clean up in one layer
Package Manager tricks
Metadata

Make sure to add ARG statements as late as possible to not invalidate the layer cache needlessly.Each ARG will be prepended to all subsequent RUN statements, i.e. building an image with the following Dockerfile docker --pull --tag foo:latest --build-arg GIT_COMMIT=46e24af6 --build-arg USERNAME=flask .
Docker Command Line Cheat Sheet
Effectively results in the following calls:
Since the git commit hash will typically change with each build the build will not make good use of Docker’s layer cache
Python
Golang
Docker swarm cheat sheet. List of all commands to create, run, manage container cluster environment, Docker Swarm!
Docker swarm is a cluster environment for Docker containers. Swarm is created with a number of machines running docker daemons. Collectively they are managed by one master node to run clustered environment for containers!
In this article, we are listing out all the currently available docker swarm commands in a very short overview. This is a cheat sheet you can glance through to brush or your swarm knowledge or quick reference for any swarm management command. We are covering most used or useful switches with the below commands. There are more switches available for each command and you can get them with --help
Read all docker or containerization related articles here from KernelTalk’s archives.
Docker swarm commands for swarm management
Cheat Sheet Docker Compose
Drivers cambridge silicon radio. This set of command is used mainly to start, manage the swarm cluster as a whole. For node management, within the cluster, we have a different set of commands following this section.
Docker Build Cheat Sheet
docker swarm init: Initiate swam cluster- –advertise-addr: Advertised address on which swarm lives
- –autolock: Locks manager and display key which will be needed to unlock stopped manager
- –force-new-cluster: Create a new cluster from backup and dont attempt to connect to old known nodes
docker swarm join-token: Lists join security token to join another node in swarm as worker or manager- –quite: Only display token. By default, it displays complete command to be used along with the token.
- –rotate: Rotate (change) token for security reasons.
docker swarm join: Join already running swarm as a worker or manager- –token: Security token to join the swarm
- –availability: Mark node’s status as active/drain/pause after joining
docker swarm leave: Leave swarm. To be run from the node itself- -f: Leave forcefully ignoring all warnings.
docker swarm unlock: Unlocks swarm by providing key after manager restartsdocker swarm unlock-key: Display swarm unlock key- -q: Only display token.
- –rotate: Rotate (change) token for security reasons.
docker swarm update: Updates swarm configurations- –autolock: true/false. Turns on or off locking if not done while initiating.
Docker swarm node commands for swarm node management
Node is a server participating in Docker swarm. A node can either be a worker or manager in the swarm. The manager node has the ability to manage swarm nodes and services along with serving workloads. Worker nodes can only serve workloads.
docker node ls: Lists nodes in the swarm- -q : Only display node Ids
- –format : Format output using GO format
- –filter : Apply filters to output
docker node ps: Display tasks running on nodes- Above all switches applies here too.
docker node promote: Promote node to a manager roledocker node demote: Demote node from manager to worker roledocker node rm: Remove node from the swarm. Run from the manager node.- -f : Force remove
docker node inspect: Detailed information about the node- –format : Format output using GO format
- –pretty : Print in a human-readable friendly format
docker node update: Update node configs- –role : worker/manager. Update node role
- –availability : active/pause/drain. Set node state.
Docker swarm service commands for swarm service management
Docker service is used to create and spawn workloads to swarm nodes.
Owasp Cheat Sheet Docker
docker service create: Start new service in Docker swarm- Switches of
docker container runcommand like -i (interactive), -t (pseud terminal), -d (detached), -p (publish port) etc supported here.
- Switches of
docker service ls: List services- –filter, –format and -q (quiet) switches which we saw above are supported with this command.
docker service ps: Lists tasks of services- –filter, –format and -q (quiet) switches which we saw above are supported with this command.
docker service logs: Display logs of service or tasksdocker service rm: Remove service- -f : Force remove
docker service update: Update service config- Most of the parameters defined in service create command can be updated here.
docker service rollback: Revert back changes done in service config.docker service scale: Scale one or more replicated services.- servicename=number format
docker service inspect: Detailed information about service.
